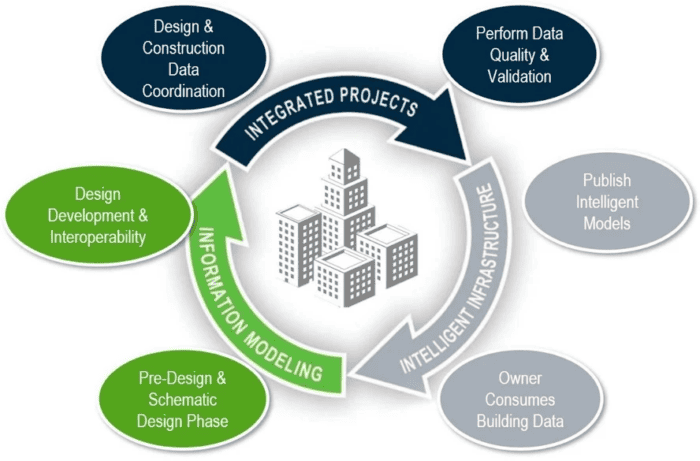
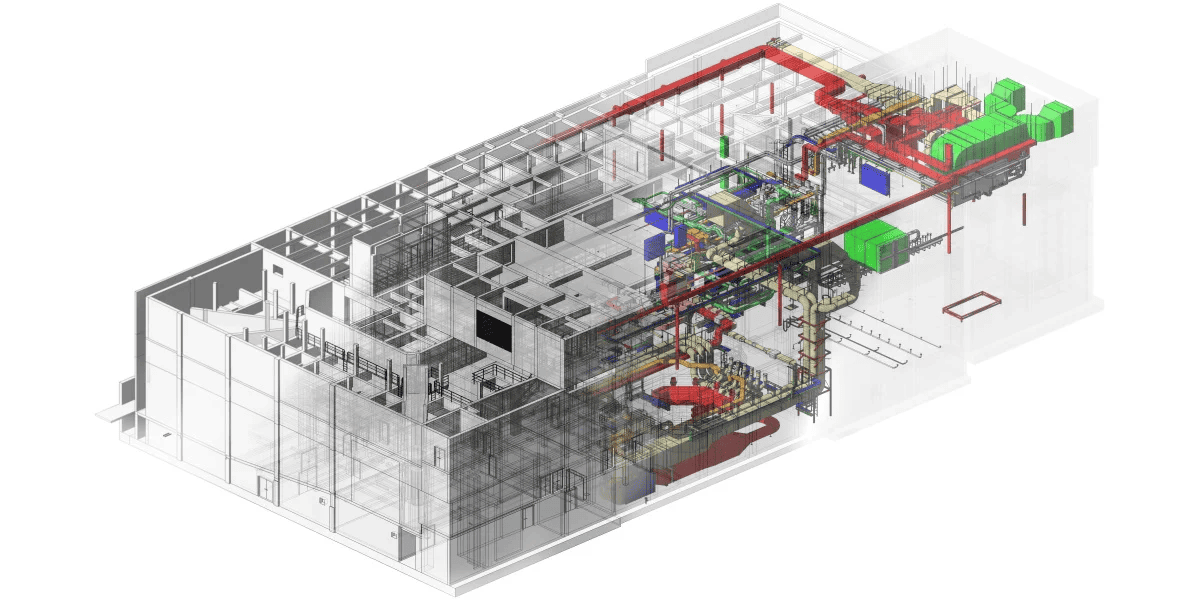
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a methodology that involves planning, executing, and managing buildings and other structures with software. Relevant building data is digitally modeled, combined, and recorded.
The technology also enables creating a virtual model (computer model) of the building, containing precise and well-defined geometry and related data required to facilitate the construction and operational activities. AEC professionals use BIM for building planning (architecture, engineering, building services, civil engineering, urban planning, railway construction, road construction, hydraulic engineering, geotechnical engineering) and facilities management.
Open BIM vs Closed BIM
To use the BIM planning methodology efficiently in a project, data exchange and communication between the involved parts need to run smoothly. To achieve this objective, architects and engineers can adopt two different approaches, Open BIM and Closed BIM:
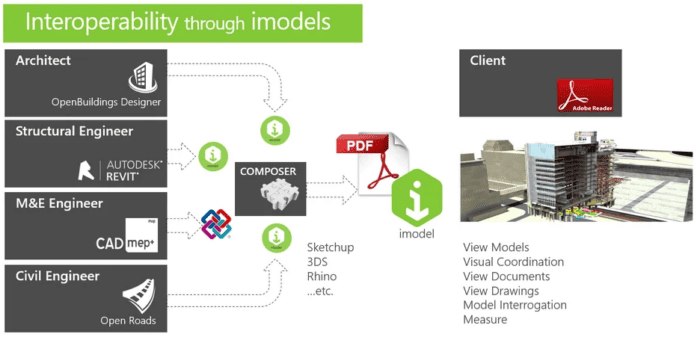
Open BIM is a data exchange strategy based on open information models – which means you can use different software in collaboration to compose a workflow. The open formats used for this purpose include IFC (perhaps the most commonly known format for BIM), IDGN, and BCF. IFC and BCF are the data formats created and maintained by buildingSmart International. IDGN is an I-model file, a dedicated container for infrastructure information exchange, developed by Bentley Systems.
Closed BIM, on the other hand, is a strategy based on closed information models. Project teams adopting this methodology need to use only one software to perform the workflow. The software to be used in a closed BIM approach should be tailored to several specialist planning disciplines, e.g., OpenBuildings Designer is an all-in-one BIM software that includes capabilities for architectural, MEP, structural, and electrical systems. In the DACH area, a well-known software used for this purpose is Speedikon* on top of MicroStation**.
The process also necessitates project teams to be put together judiciously to facilitate optimum software utilization by as many specialist planning disciplines as possible.
The Best BIM Approach for You
Both methods provide some common advantages such as:
- Improved data quality, since all the project related information go back to a shared database and is continuously synchronized
- Immediate and continuous availability of current and relevant project data
- Enhanced exchange of information between project stakeholders
- Constant data preparation and comparison across the entire building life cycle, thereby enhancing the planning process’s productivity in terms of costs, deadlines, and quality.
Advantages of Open BIM
Open BIM is a software family independent and cross-system data exchange, mostly using the IFC file format (Industry Foundation Classes). IFC stands for the cross-manufacturer and cross-platform exchange of building model data (BIM data). IFC, as a file format, is the technical standard for model and component-oriented planning. Among the many advantages it offers, the most significant one is the freedom to choose planning partners or planning programs of one’s choice. The Open BIM approach enables every specialist planner to work with specific BIM software of his/her choice and share files with multiple software via open file standards. In this process, the project partners transfer only partial models and the related information with each other. For example, the structural engineer receives only supporting structure-related information from the architect.
In Open BIM every planner plans his/her specialist model, ensuring improved transparency and traceability of responsibilities. This approach provides checked and fixed planning statuses to the planning partner as per the specified schedule. Planners can rely on these statuses and refer to them in the event of discrepancies. In the Open BIM process, every planner has clearly outlined liability areas, enabling them to make changes only in the building parts they are responsible for.
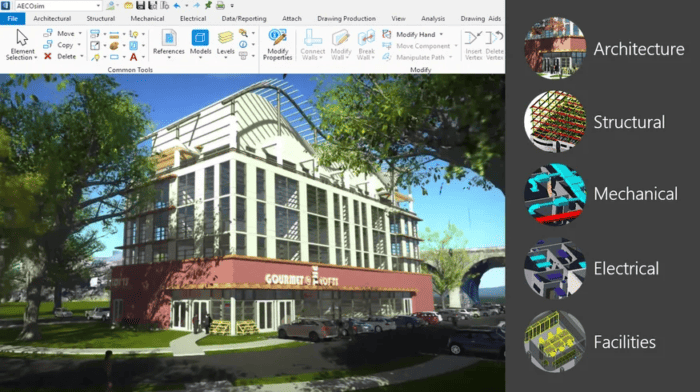
OpenBuildings Designer – the BIM software
OpenBuildings Designer is an all-in-one BIM software to help AEC professionals execute their contract tasks seamlessly. There is no doubt that this comprehensive software can help you successfully deliver Open BIM requirements and Closed BIM requirements. You can also achieve unrestricted data exchange in various ways, thanks to the integrated MicroStation functions in OpenBuildings Designer. As a rule, the file size always remains within a well manageable range. Thus, nothing stands in the way of successful collaboration on BIM projects.
Advantages of Closed BIM
This approach aims to have the smoothest possible data exchange. When using Closed BIM, all the stakeholders work simultaneously on a single building model and use the respective software manufacturers’ proprietary data format. Since this is only possible with the programs of a software family, everyone involved must use them. This “closed” way of working can be advantageous if the same team always works together on different projects. Reliability and trust are essential within the team. On the flip side, when working together on a model, sometimes the team members’ liability areas can undoubtedly become blurred.
For example, the structural engineer can change the column positions, or the in-house technician can insert openings without consulting other specialist planners. However, these adjustments may impact further specialist planning, which needs to be corrected.
Open BIM vs Closed BIM – Making the Right Choice
The way of working is decisive. Fundamental to both approaches is that project stakeholders involved in the planning should determine in advance which information is to be transferred and when. While comparing Open BIM with Closed BIM, each of the working methods offers its unique advantages.
Closed BIM is an optimal solution for those who always cooperate with the same partners under the same responsibility and liability conditions. On the other hand, the use of Open BIM – thanks to its great flexibility and open and agile data formats – is more suitable for building professionals needing a wide range of data transfer options.
BIM Leads to Error-free and Sustainable Life Cycles
In recent years, various studies have shown that digital construction before physical construction and modeling and virtual reality help identify conflicts and incorrect specifications at an early stage and result in saving essential resources. Therefore, consistent digitization across all service phases with BIM helps project members work together precisely, flexibly, and efficiently.
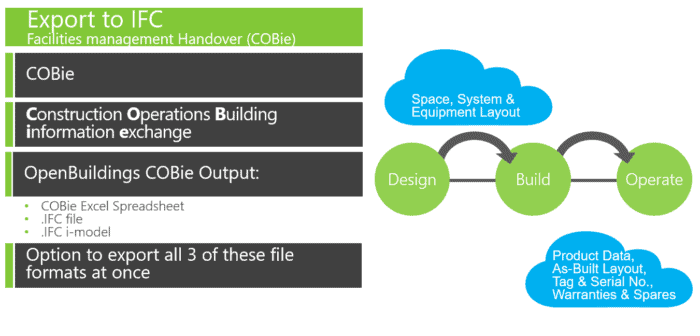
Creating a BIM Project is the Virtual Prerequisite for Creating a Digital Twin
A digital twin is a virtual representation of real-world objects and processes synchronized at a specific frequency and fidelity to the original. Digital twins transform businesses by accelerating holistic understanding, optimal decision-making, and effective action. The digital twin is the update of a BIM model over the entire lifecycle of an asset, whether it is a building, a road, or a tunnel.
Start with your own BIM project now!
*Speedikon – Building design and documentation software
**MicroStation – Modeling, documentation, and visualization software