ADINA is a unique tool to perform coupled CFD and structural analyses, and we are strengthening the program continuously for such applications. Here we focus on the analysis of a manifold and consider the turbulent fluid flow through the manifold, the temperatures in the fluid and the structure, and the stresses in the structure.
A particular capability needed here, with the meshes used, is the automatic coupling of the temperature between totally different meshes.
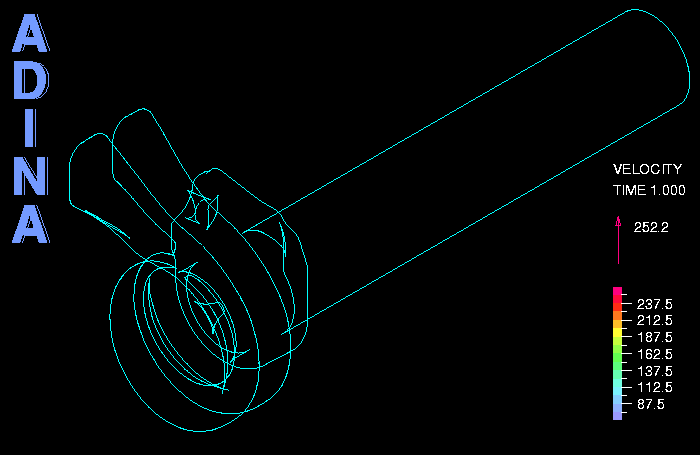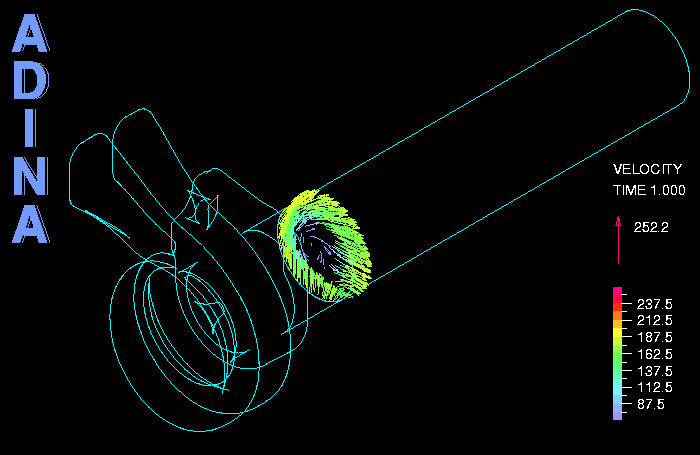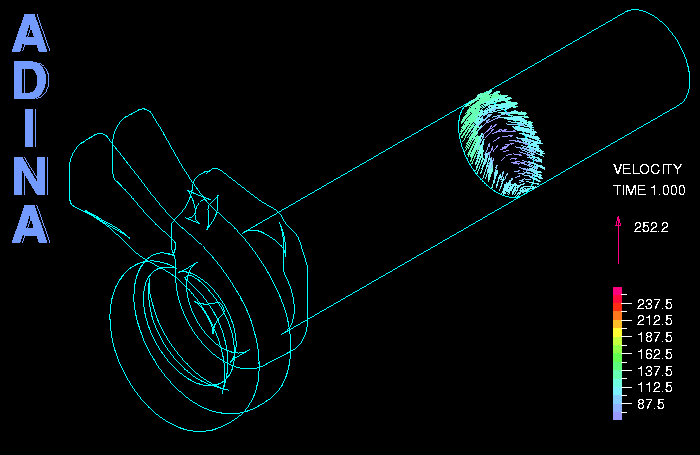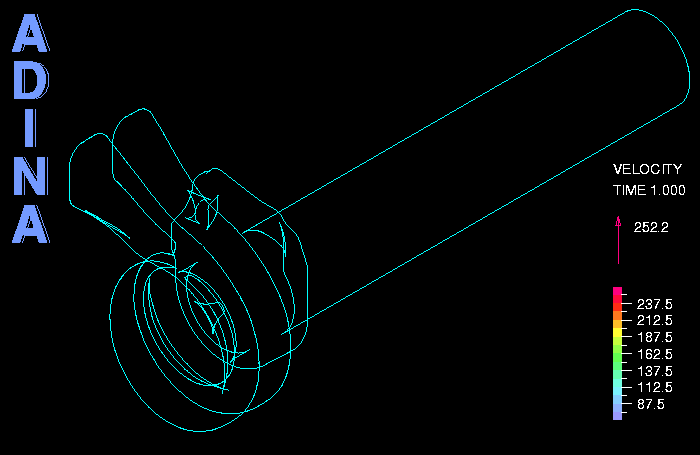
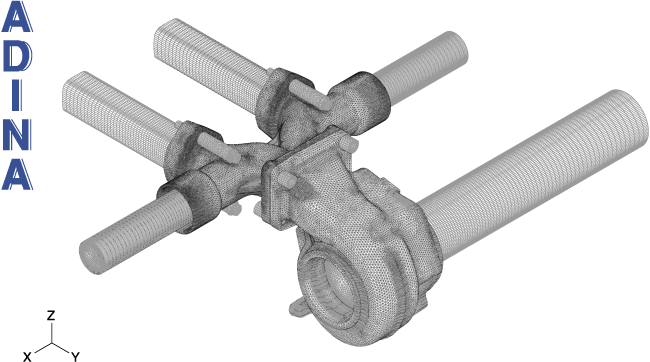
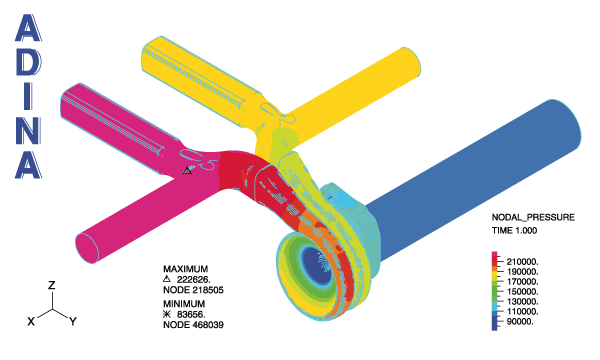
The figures below show the model of the fluid and solid, and some temperature and stress results. The movie above shows some velocity results in the outlet. The model contains a total of about 5 million elements. For the fluid the k-omega turbulence model is used. The Re, Pe and Pr numbers are Re = 0.74 x 105, Pe = 0.54 x 105, Pr = 0.73.
Mesh used for the complete model
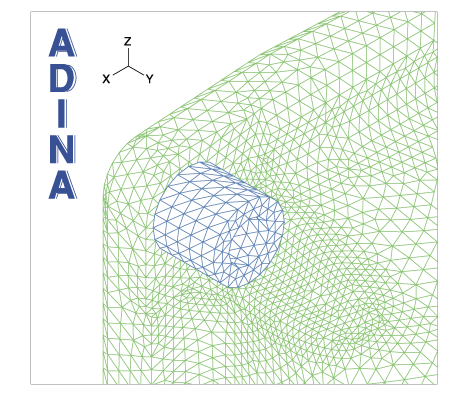
Detail showing mesh mismatch
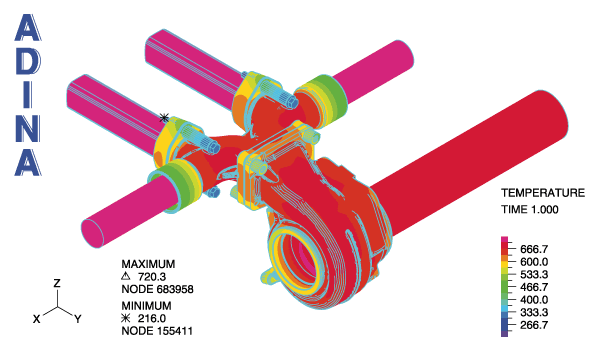
Plot of temperature in the fluid and solid
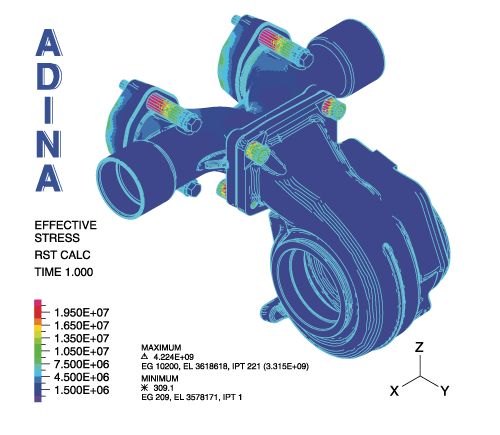
Plot of effective stress in the solid
Plot of pressure in the fluid
In the model, the contact and gluing algorithms are used.
This model was solved with ADINA, version 8.5, because we have implemented some significant computational improvements that are used in this solution.