Sweden has 10 nuclear power reactors providing nearly half of its electricity. Due to the current concern for optimal energy sources, many Swedes consider nuclear power a good option when competitiveness and environmental impact are taken into account. As nuclear power carries the risk of toxic pollution, the safe, efficient operation and maintenance of the nuclear reactors is very important.
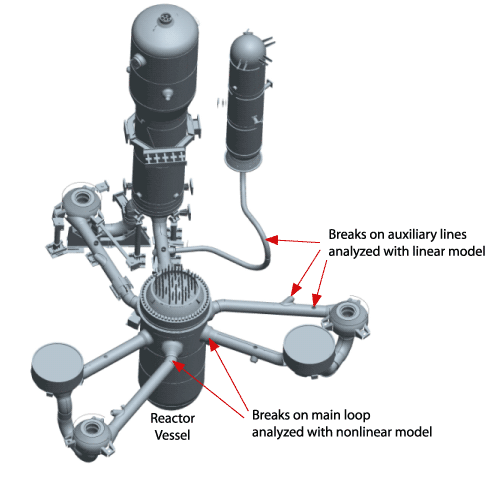
Because of its reliability and solution effectiveness, ADINA is used in many reactor studies in Sweden. In this News we feature one such study of the effect of a pipe break in a pressurized water reactor. The study was conducted by Onsala Ingenjörsbyrå (Onsala Engineering AB, Sweden) which performed the work under a contract from Ringhals AB. Figure 1 below shows the nuclear reactor considered.
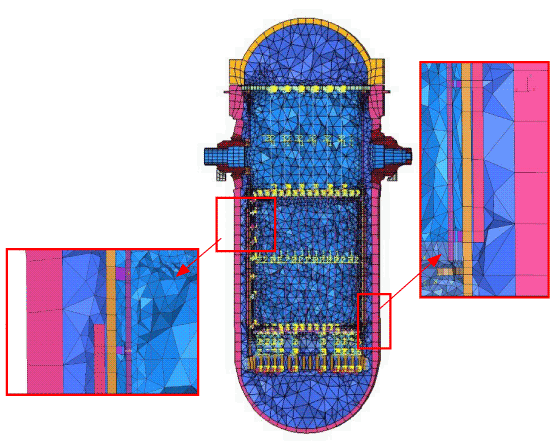
The geometry for the entire model was created in Pro/Engineer, while the mesh and the boundary condition sets were created in ANSA. The complete model consists of more than 800,000 solid, structural and fluid elements with 55,000 nodes in contact, a total of 1.6 million degrees of freedom. The model is depicted in Figure 2 below, and part of the mesh used to model the reactor vessel is shown in Figure 3.
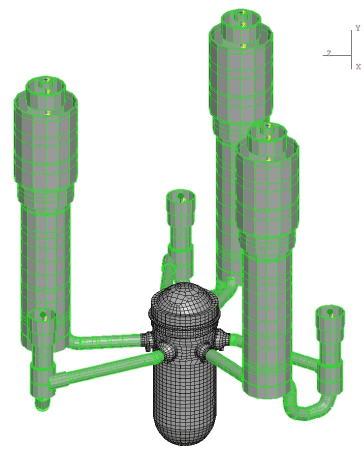
Fig. 3. Part of the mesh consisting of solid, structural and fluid elements
used to model the reactor vessel
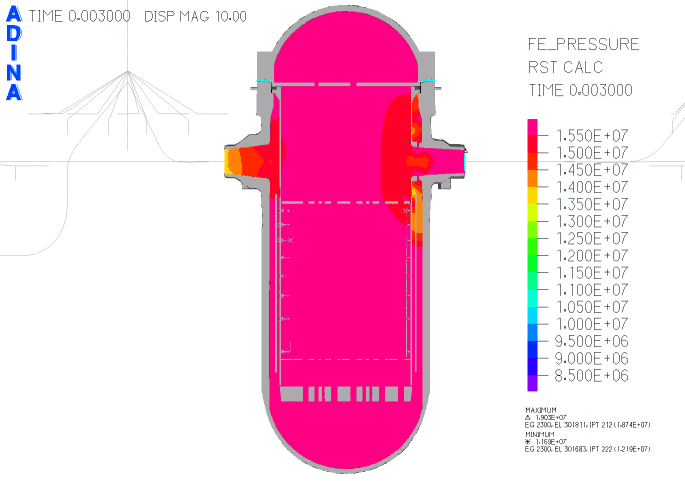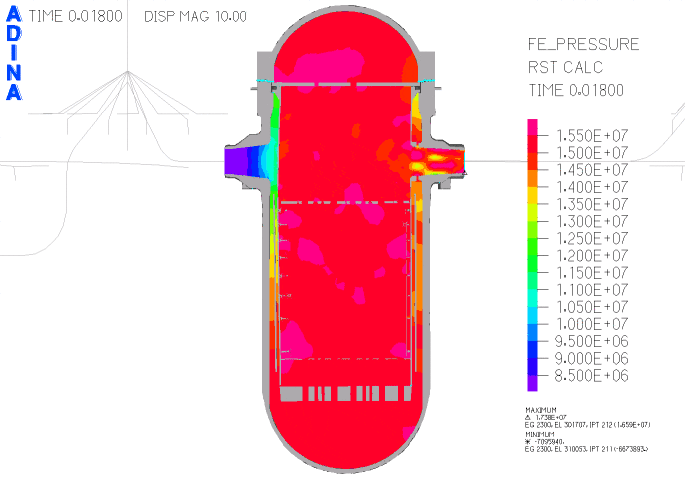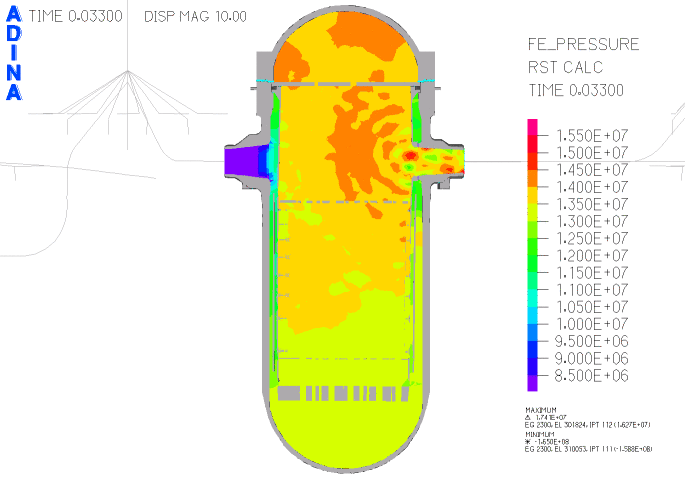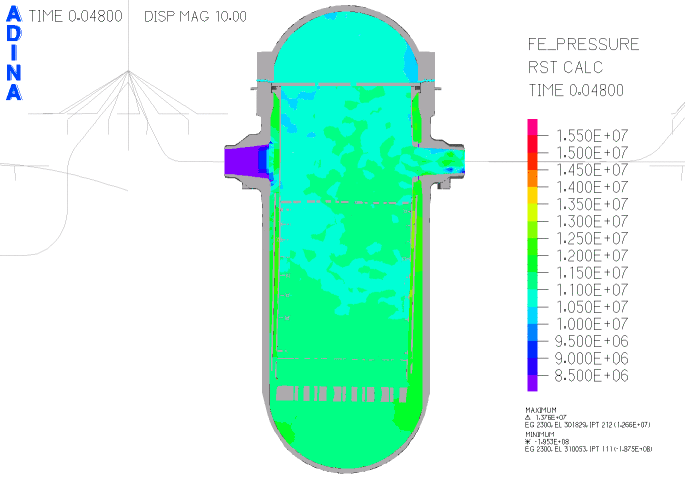
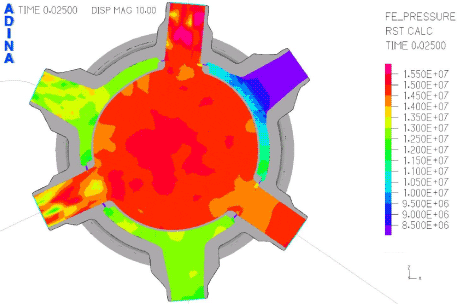
Fig. 4. Pressure plot in section of reactor vessel
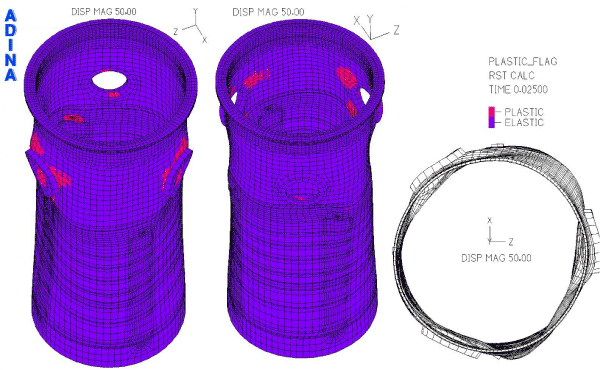
With the results of the analysis, Onsala engineers were able to predict the structural response of the reactor vessel due to the pipe break (Figure 5 below) as well as the maximum bolt forces.
Fig. 5. Predicted plastic regions in reactor vessel
While already yielding many useful results, of course, the model can be further developed for additional analyses.
This study illustrates, only to some degree, the powerful capabilities available in ADINA for dynamic linear and nonlinear analyses, including fluid-structure interactions. Many different types of analyses can be performed in a very effective and reliable manner, a requirement particularly important in studies of reactors.
Courtesy of Onsala Ingenjörsbyrå AB