Estimation of the support required to stabilize a tunnel excavation, especially in the vicinity of the face, is essentially a four-dimensional problem. Time-dependent weakening of the rock will compound the three-dimensional redistribution of forces around the excavation. Given these constraints, it is valuable to have a general but still relatively simplified appreciation of the nature of the interaction between the rock-mass and the installed support. The Convergence-Confinement method has been developed for this exact need.
The Convergence-Confinement Method is a basic and commonly used tool for underground support structures in conventional tunneling during the preliminary stage of design. It was initially an analytical method for circular tunnels. Based on the analysis of stresses and strains around a tunnel, the Convergence-Confinement Method provides an insight into the interaction between the support and the ground by means of a plane-strain model of the tunnel excavation. It provides meaningful numerical results in a 2D analysis framework.
Main Principles
The Convergence-Confinement Method is a procedure that allows the load imposed on a support installed behind the face of a tunnel to be estimated. When a section of support is installed in the immediate vicinity of the tunnel face, it does not carry the full load to which it will be eventually subjected. A part of the load that is redistributed around the excavation is carried by the face itself. As the tunnel and face advance (i.e., away from the installed support), this ”face effect” decreases, and the support must carry a greater proportion of the load that the face had carried earlier. When the face has moved well away from the support in question, it effectively carries the entire design load.
The basis of the Convergence-Confinement Method has been perfectly summarized by Carranza Torres and Fairhurst (2000), from which we have extracted the upcoming elements illustrating the main principles of the Convergence-Confinement Method as shown in Figure 1:
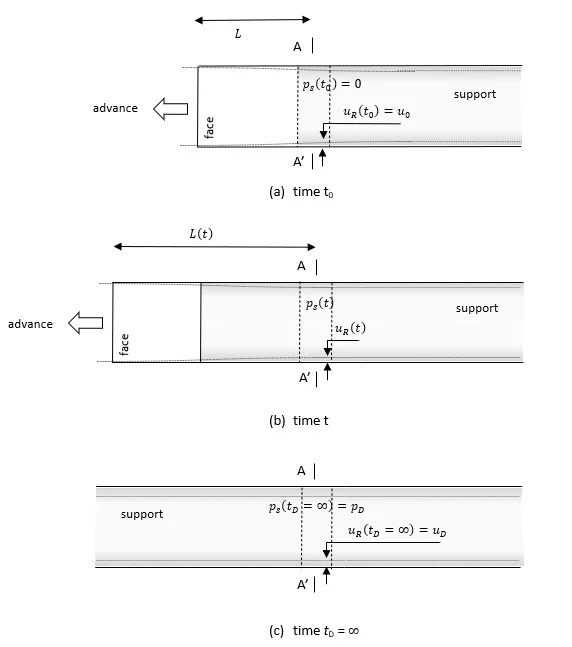
- The situation at the initial time t0, when the lining is installed at section A-A’, is represented in the upper sketch (Figure 1a). At this instant, the section is located at a distance L from the face and the ground has converged radially by the amount
. It is assumed that, provided the face does not advance, the rock-mass transmits no load to the support – i.e.,
at this stage.
- As the tunnel advances to the left, the ground and the support (at section A A’) deform together, and the support receives part of the load that the face had been carrying previously. Figure 1b shows the situation at a time t when the section is located at the distance L(t) from the face. At that moment, the ground has converged the amount
and the rock-mass transmits the pressure
to the support.
- Once the face of the tunnel has moved ahead far enough (Figure 1c), the ground-support system at the section A-A’ is in equilibrium and the support carries the final (or design) load
. At this time,
, the effect of the face has disappeared, and the support and ground have converged together to the final amount
.
Figure 1: Loading of the support at section A-A’ due to progressive advance of the tunnel face (after Carranza and Fairhurst, 2000).
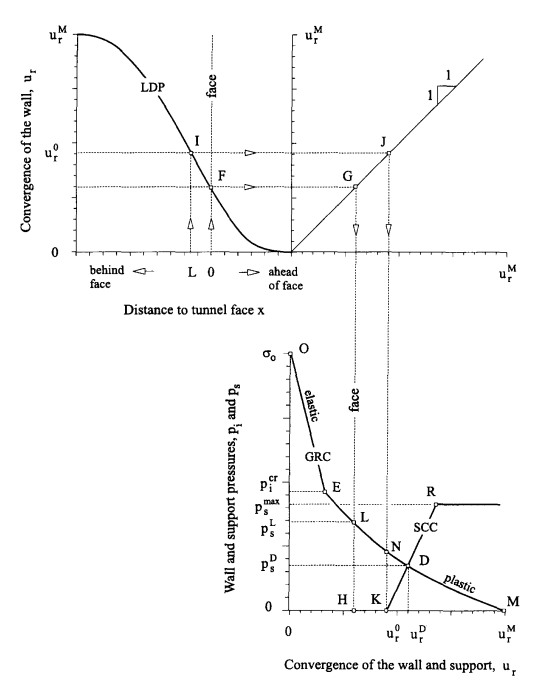
Figure 2: Schematic representation of the Longitudinal Deformation Profile (LDP), Ground Reaction Curve (GRC), and Support Characteristic Curve (SCC) (after Carranza and Fairhurst, 2000).
As can be seen from Figure 1, the determination of the load transferred to the support requires an analysis of the interaction of the load-deformation characteristics of the elements comprising the system:
- The tunnel as it moves forward
- The section of excavation perpendicular to the tunnel axis and
- The support is installed at that section.
As illustrated in Figure 2, the three basic components of the Convergence-Confinement Method are therefore:
- The Longitudinal Deformation Profile (LDP)
- The Ground Reaction Curve (GRC) and
- The Support Characteristic Curve (SCC).
Longitudinal Deformation Profile
The LDP is the graphical representation of the radial displacement that occurs along the axis of an unsupported excavation – for sections located ahead of and behind the face. It enables the user to determine the amount of radial displacement that will take place at the tunnel boundary (and corresponding amount of rock stress release) before the installation (and therefore associated loading) of stiff support will take place.
LDP is used to calibrate the staged plane strain 2D model in which the inner tunnel core will be replaced by incrementally relaxing boundary tractions to simulate a progressive reduction of a “fictitious” internal support pressure applied at the tunnel wall:
where 0 is the initial stress state and is the deconfining rate.
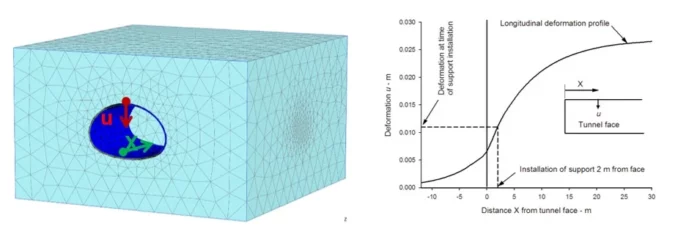
For uniform or isotropic initial stress conditions and circular tunnel cross-sections, the LDP can be calculated using axisymmetric models or analytical formulas as introduced by Panet (1995). However, for most situations (anisotropic state of stresses, non-circular tunnel cross-section, etc.), three-dimensional analyses will provide the most accurate LDP curves (see Figure 3).
Figure 3: Use of PLAXIS 3D numerical analysis for the obtention of the LCD for a horseshoe tunnel.
Such analyses could advantageously be set up using the PLAXIS Tunnel Designer functionality to ease the creation of the 3D geometry from a simple 2D cross-section definition and speed up construction stage setup where the incremental tunnel construction process must be accurately taken into consideration.
Ground Reaction Curve (GRC)
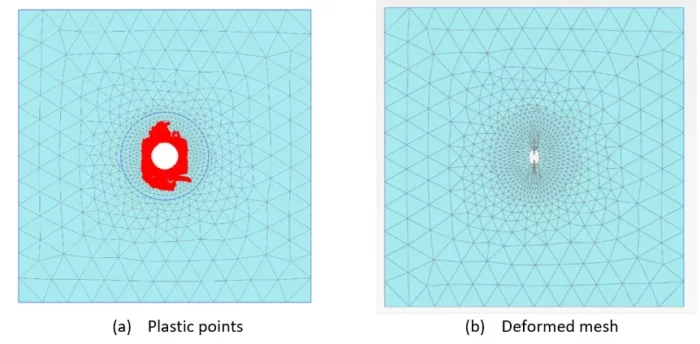
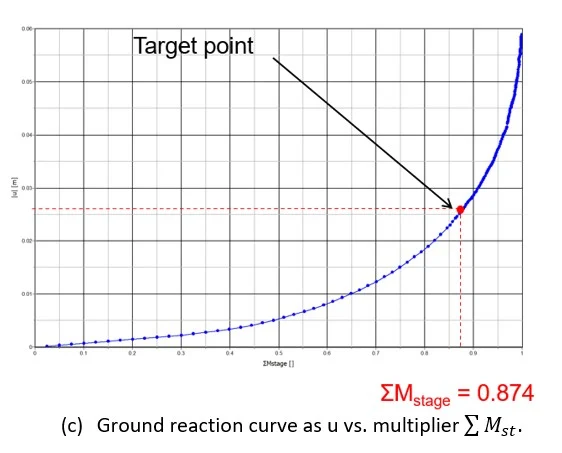
The Ground Reaction Curve can simply be obtained by running a PLAXIS 2D plane strain analysis with the consideration of a full tunnel excavation without any means of support. Such analysis will enable the monitoring of the tunnel wall radial displacement versus the staged construction multiplier 
Figure 4: PLAXIS 2D for the determination of the Ground Reaction Curve.
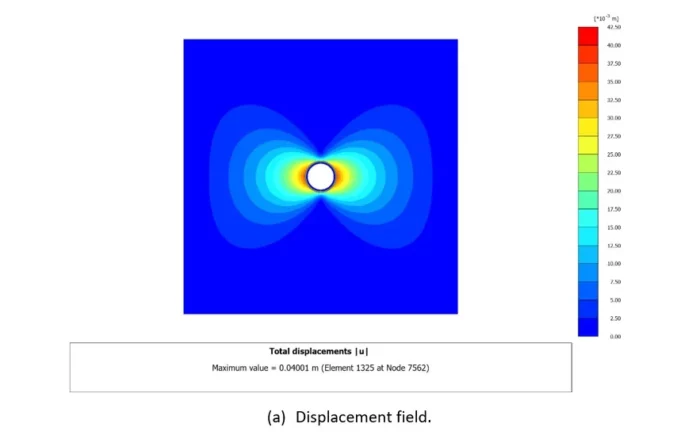
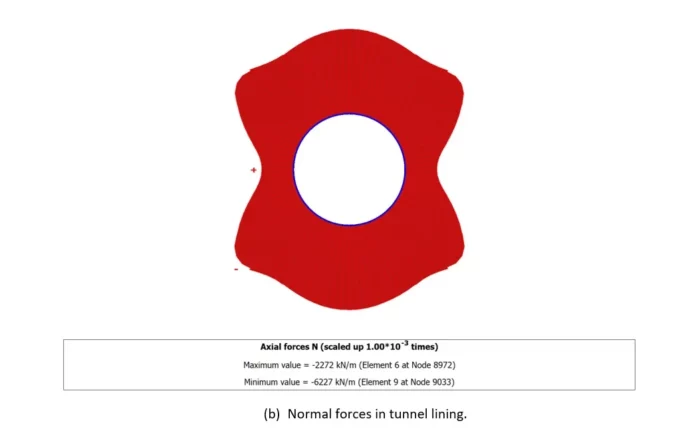
Figure 5: PLAXIS 2D analysis results after activation of the tunnel support.
Support Characteristic Curve (SCC)
The obtained GRC will then be used to evaluate the equivalent deconfinement level that will provide the same radial tunnel wall displacement as given by the LDP at a distance L from the front tail where the support is meant to be activated.
The Support Characteristic Curve will be implicitly provided in a separate and similar 2D plane strain analysis with the additional activation of the tunnel support at the appropriate level of confinement found during previous analysis (as deduced in Figure 4c). An example of such type of 2D analyses is presented in Figure 5.
References
Carranza-Torres C. and C. Fairhurst C. (2000) – “Application of the Convergence-Confinement Method of Tunnel Design to Rock Masses That Satisfy the Hoek-Brown Failure Criterion” – Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, Vol. 15, No. 2, pp. 187-213.
Panet M. (1995) – “Le calcul des tunnels par la méthode convergence-confinement“ – Presses de l’Ecole Nationale des Ponts et Chaussées, Paris (in French).

 . It is assumed that, provided the face does not advance, the rock-mass transmits no load to the support – i.e.,
. It is assumed that, provided the face does not advance, the rock-mass transmits no load to the support – i.e.,  at this stage.
at this stage. and the rock-mass transmits the pressure
and the rock-mass transmits the pressure  . At this time,
. At this time,  , the effect of the face has disappeared, and the support and ground have converged together to the final amount
, the effect of the face has disappeared, and the support and ground have converged together to the final amount  .
.