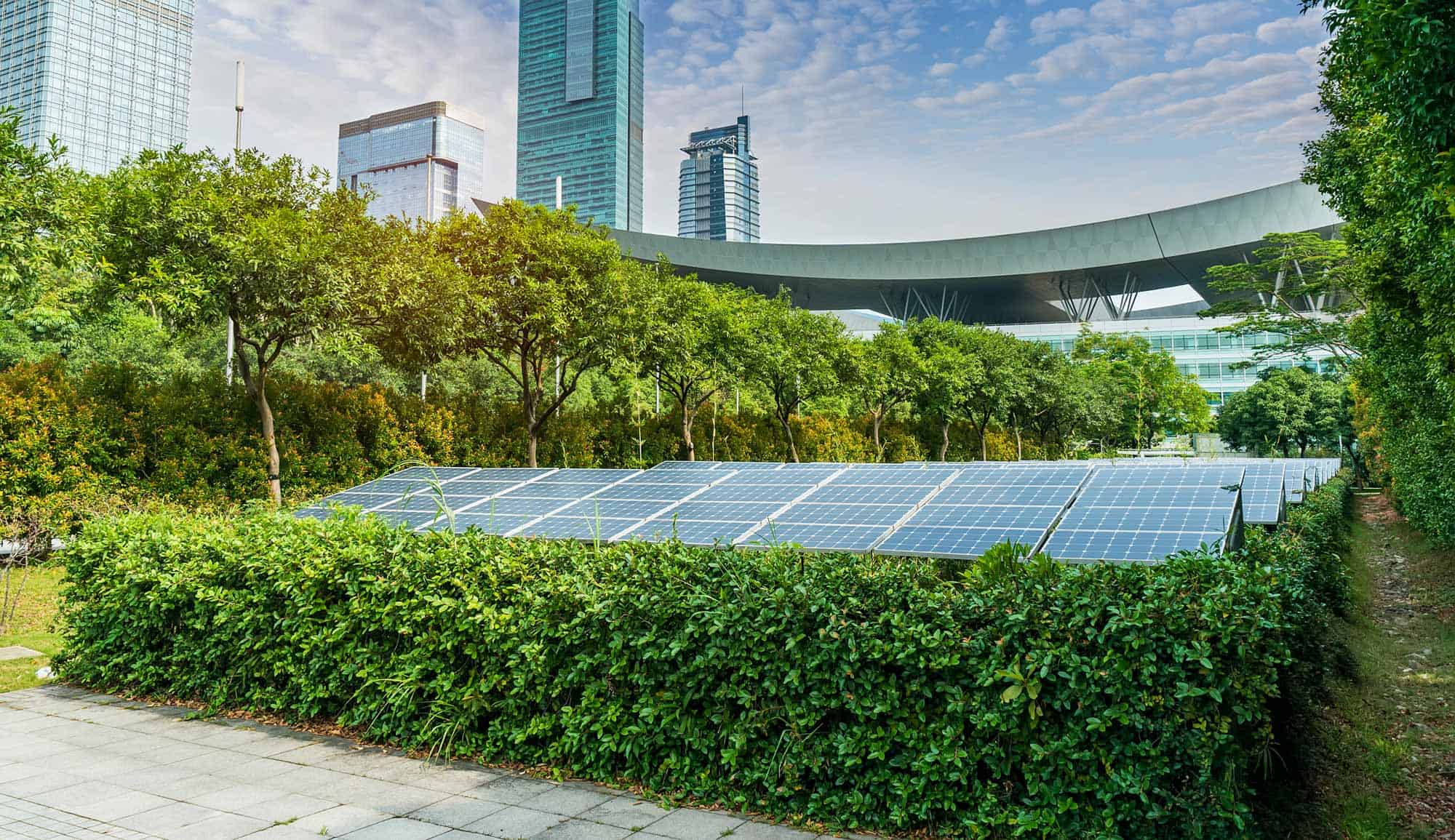
Solar energy is growing source of renewable power. Engineers need to examine different options for their solar energy installations based on a variety of factors.
There are several types of photo-voltaic mounting structures:
- Ground-mounted
- Roof-top
- Pole-mounted
- Floating solar
The first three will be covered in this and following articles in the series. You can find out more regarding floating solar structures in this webinar: Floating Solar Farms.
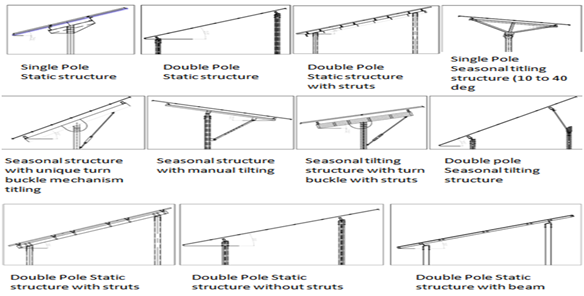
Figure 1: Various configurations of solar systems

PV Mounting Structure Modeling with STAAD.Pro
The panel that generates the electrical energy may be the principal component in these solutions, but to provide a stable platform on which the unit can operate means that a suitable structural frame is required. This is where STAAD.Pro structural analysis software can provide designers with a system to design their support structure using tools like:
- Advanced modeling
- Section assignment
- Loads and techniques for load application
Let’s start with the first reason, advanced modeling.
Advanced Modeling for Solar Structures
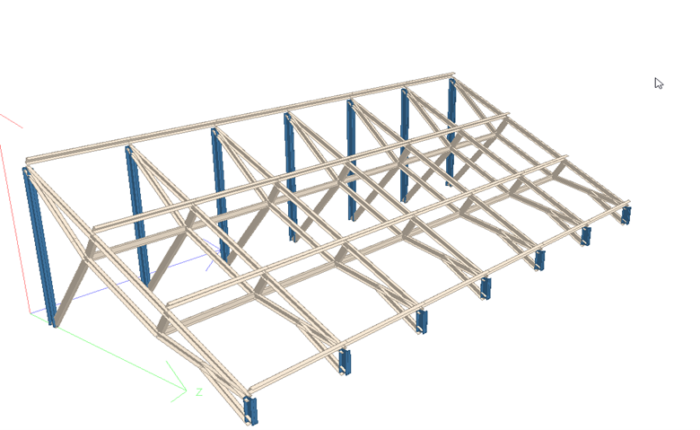
Solar supporting structures tend to be typical. These flexible frame-type structures are predominantly modeled in the analytical modeler of STAAD using the Structure Wizard. They may also be modeled in the regular STAAD GUI using node, beam elements, and commands like Translation Repeat to complete the structural model. Wherever possible, temperature straining effects should be handled by assigning axial releases in the STAAD model.
Figure 3: STAAD model of a typical photo-voltaic structure.
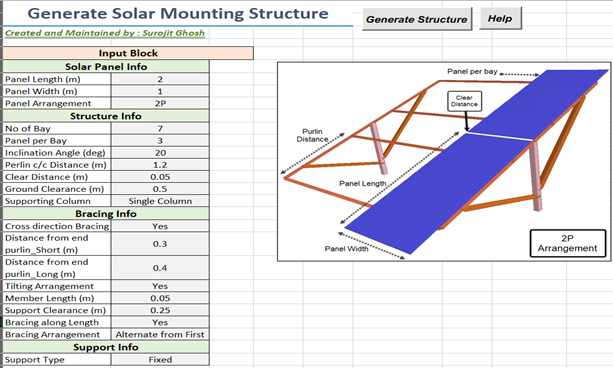
With OpenSTAAD, you can take advantage of API and link external tools like Microsoft Excel with STAAD to generate the model in just a few seconds. Parametric model generation by custom template files is quite handy and saves a lot of time. Bentley technical experts create custom files using API to help users automate workflows.
Figure 4: STAAD model generation using API of a typical PV structure.
The modeling, analysis, and design techniques are similar for a roof-top mounted structure as well as a ground-mounted structure. Still, due to high wind load intensities, the structural steel material and structural steel profiles used will vary. Structural steel, either hot-rolled or cold-formed, is the preferred choice for designing solar PV supporting structures.

In solar projects, especially ground-mounted solar structures, cold-formed sections are usually chosen, because they are:
- Cost-effective
- Lightweight
- Easy to assemble and erect on site
There are different structural arrangements and mechanisms in various projects. The tilting angle can be static at a fixed angle or change automatically or manually at different seasons. The configuration must be modeled accurately, as the wind load application depends on the inclination.
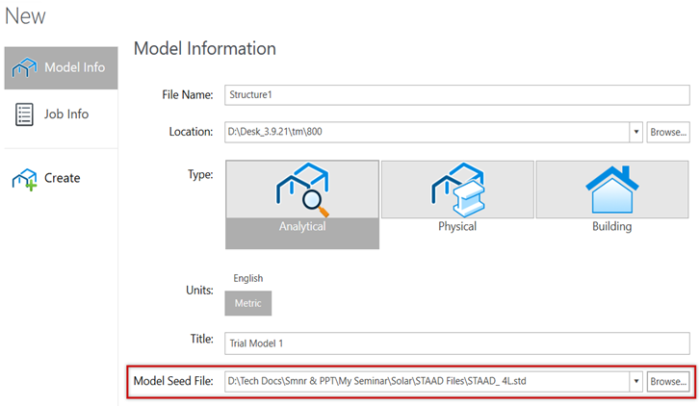
Solar supporting structures tend to be typical in configuration. So the workflow usually involves performing repetitive tasks, such as the reuse of section assignments, beta angles, load cases, and combinations. Creating a seed file option is available in STAAD because Update 6 enables the instant replication and reuse of data like material properties, section profiles, load cases and combinations.
Figure 7: Seed file use in STAAD
In the following blog posts, we’ll take an in-depth look at the next two reasons why STAAD.Pro is your software of choice for PV mounting structures:
- Section assignment
- Loads and techniques for load application