Navigating the Increasing Challenges Facing the Global Water Industry
Water and wastewater projects are crucial for ensuring access to clean water, efficiently managing water resources, and promoting environmental sustainability. The water industry must overcome numerous complex challenges in the coming years due to rapid urbanisation, severe climate changes, rising customer demands, and emerging digital technologies. Governments, organizations, and communities worldwide are investing in various technologies to address these challenges.
The Benefits of Implementing BIM in Water and Wastewater Projects
Designing a water treatment plant is challenging and requires both smooth collaboration between multidiscipline teams and efficient management of several regulatory and economic aspects. Building information modeling (BIM) effectively overcomes these challenges while helping to manage the whole lifecycle of a water treatment plant, from planning and design through construction and maintenance. It can create a digital representation of a facility’s physical and functional characteristics, facilitating information creation and management throughout its lifecycle.
Here are some key benefits of implementing BIM in water industry projects:
Integrated Design and Coordination
BIM facilitates collaboration among multiple design disciplines and allows for integrated design and coordination, ensuring all components work together seamlessly. Clash detection can identify conflicts between systems, such as pipes, pumps, valves, and electrical conduits, minimizing design errors and rework.
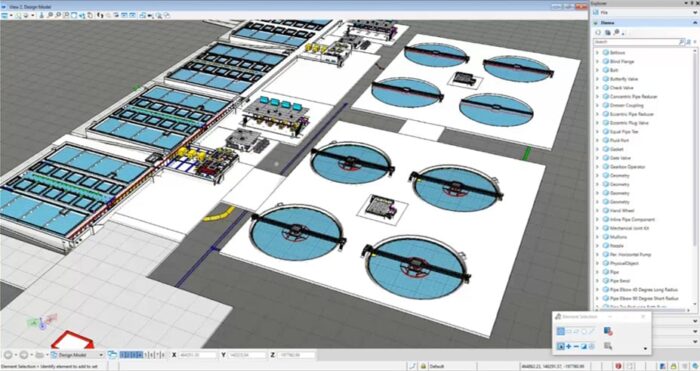
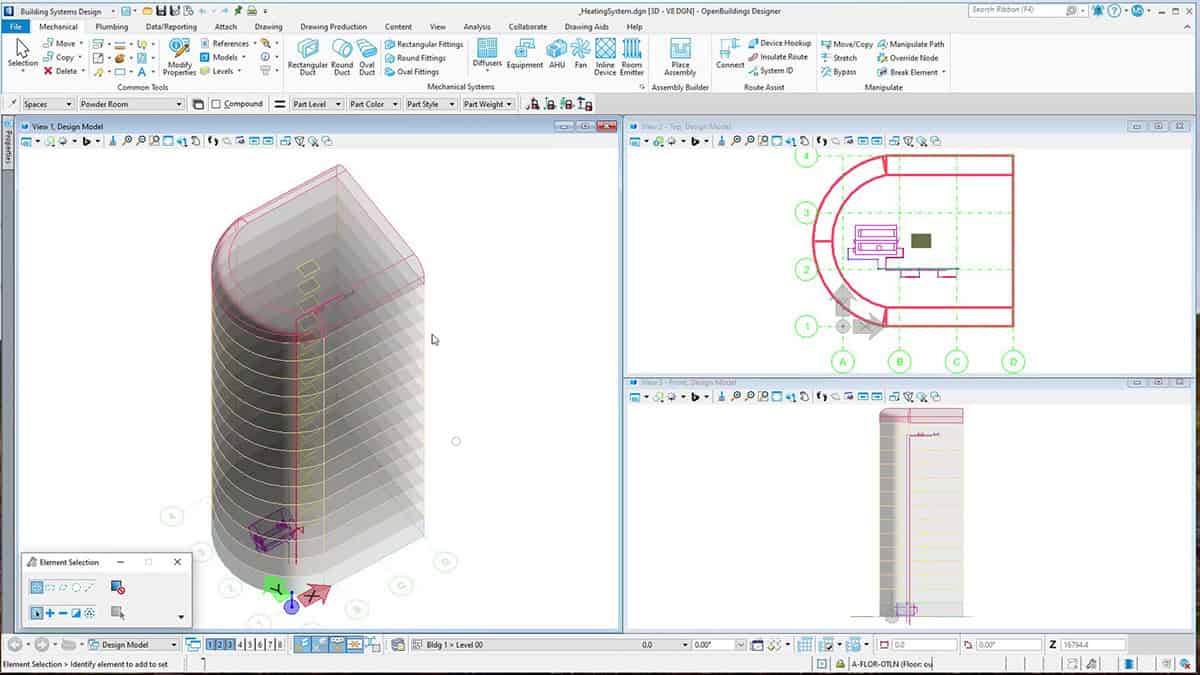
3D Visualization and Modeling
BIM provides a 3D representation of water treatment plants, allowing stakeholders to improve their understanding of project layouts, equipment placement, and spatial requirements. Visualization helps identify potential design issues, optimize space utilization, and ensure efficient workflows during construction and operation. Intelligent project deliverables in the form of drawings, reports, and other documentation are derived and synced with the 3D models from conceptual stages to project completion and handover.
Equipment and System Optimization
BIM enables placing and sizing equipment within the treatment plant. By simulating the flow of water and processes, engineers can optimize the design and layout of treatment units, pumps, filters, and other components. As a result, engineers will achieve optimal performance, reduce energy consumption, and enhance the overall efficiency of the plant.
Energy Efficiency
BIM can help identify opportunities for energy optimization in water treatment plant design and operation. Through energy modeling and simulation, BIM can evaluate different design alternatives, assess energy consumption, and identify energy-saving measures such as optimized equipment selection, HVAC systems, and lighting, as well as renewable energy solutions like solar or wind power.
Quantification and Cost Estimation
BIM integrates with quantity takeoff software to automate material quantity extraction, streamlining the process of generating accurate cost estimates and bills of quantities for procurement and tendering purposes.
Construction Sequencing and Phasing
BIM facilitates the creation of construction sequencing and phasing plans. Contractors can simulate the construction process, identify potential clashes or conflicts, and optimize schedules to minimize disruptions during construction. This work helps with planning equipment installation, determining access routes, and coordinating construction activities.
Facility Management and Maintenance
BIM serves as a valuable tool for facility management and maintenance, as it can store critical information about equipment specifications, maintenance schedules, operating manuals, and asset locations. This data assists operators in managing maintenance activities, tracking equipment performance, and ensuring efficient operations.
Data Integration and Interoperability
BIM can integrate various data sources and systems to design and deliver water treatment plants. It enables interoperability between BIM software and other applications, such as SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems and asset management software. This integration enhances data exchange, improves decision-making, and supports long-term operation and maintenance activities.
Accelerating Digital Innovation is the Key to Achieving Water Sustainability and Resilience Worldwide
Embracing BIM has been a valuable step in the digital transformation of the water industry. Now, it is time for forward thinkers to advance their BIM workflows beyond design and construction and discover new ways to use collaborative data models in operational strategies, including digital twin adoption. Many water utilities have already implemented digital twins in their water treatment plant projects, thus tying in with their commitment to accelerate digital transformation.
A digital twin of a water treatment plant is a virtual representation of the physical water treatment plant, which is created by combining real-time data, advanced modeling, and simulation techniques. A digital twin allows operators and engineers to monitor, analyze, and optimize the plant’s performance in a virtual environment, enhancing operational efficiency, improving maintenance practices, and enabling data-driven decision-making. It provides a powerful capability for optimizing plant performance, ensuring water quality, and enhancing sustainability in the water treatment industry.
The future of digital twins in the water industry looks promising. Ultimately, wider adoption will depend on the readiness of the industry to go through digital transformation and the maturity of the technology itself.
To learn more about harnessing BIM to design a better water treatment plant, check out our on-demand webinar series.