Infrastructure isn’t quick to evolve. Its sheer scale, cost, and complexity can make change painfully slow. But every so often, a person, an idea, or a tool cuts through – shifting how people see, plan, or act. Sometimes it’s a light bulb moment; other times, it’s a slow burn that catches fire. This is a collection of those turning points from across the Bentley Systems ecosystem – stories where possibility triumphed over inertia, and digital technology became a catalyst for change.
1. EchoWater’s $400 Million Saving
 Renderining of the EchoWater project area. Credit: Regional San/Project Controls Cubed
Renderining of the EchoWater project area. Credit: Regional San/Project Controls CubedWhat changed? Digital twins proved their worth in billion-dollar public works.
The moment: Stakeholders on the billion-dollar upgrade to California’s EchoWater wastewater treatment facility weren’t convinced that modeling the construction process digitally would help them deliver the project on schedule and avoid cost overruns. So Jeff Campbell and Serelle Corn, the married co-founders of Project Controls Cubed, used Bentley’s SYNCHRO software to create a 4D animation of the project, on their own time and dime. During their presentation and just 30 seconds into their video, the stakeholders spotted a critical flaw in the construction sequence that would have cost tens of millions to fix if it had been caught too late. Just like that, digital twins went from novelty to mandatory, and the project finished on time and an astonishing $400 million under budget.
Full story: When Jeff met Serelle: An Infrastructure Love Story
2. “The Bobcat Won’t Fit”
 Looking at Freeform’s SYNCHRO 4D model of Crossrail’s Moorgate Shaft, it was clear to an experienced digger operator that there wouldn’t be sufficient room to maneuver. Image courtesy of Freeform.
Looking at Freeform’s SYNCHRO 4D model of Crossrail’s Moorgate Shaft, it was clear to an experienced digger operator that there wouldn’t be sufficient room to maneuver. Image courtesy of Freeform.What changed? Confidence in the power of digital rehearsal to unite expertise.
The moment: During a planning review for London’s Crossrail project, engineer James Bowles was walking through a construction sequence in SYNCHRO 4D at the Moorgate shaft site when a veteran Bobcat digger operator spoke up. “You can put me in that hole,” he said, pointing at the model, “but I’ll be in there for six months.” The digital rehearsal had surfaced a spatial constraint that paper plans couldn’t convey. Because it was caught early, engineers were able to redesign the shaft – avoiding a major delay and saving millions. The Crossrail project delivered London’s Elizabeth Line, the British capital’s newest rail line connecting the city center to its suburbs in the east and west, including Heathrow Airport. Since it opened in 2022, ridership has surpassed 546 million journeys.
3. Digital Twins at the Heart of Fusion Power
 Inside view of the ITER (International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor) assembly hall, showing complex machinery and yellow scaffolding structures for tokamak construction.
Inside view of the ITER (International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor) assembly hall, showing complex machinery and yellow scaffolding structures for tokamak construction.What changed? Planning for ultra-complex infrastructure embraces immersive, visual understanding
The moment: At the world’s most ambitious fusion energy project, traditional planning tools struggled to capture the scale and complexity of construction. Dubbed the “reverse Tower of Babel,” the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) brings together 35 nations to prove that fusion energy- which replicates the reactions that take place inside the sun and make it shine and heat our planet- can be a practical and effectively limitless source of carbon-free energy. Lynton Sutton, working with Bentley’s SYNCHRO 4D software, built an ongoing digital rehearsal that made the entire process visible, step by step. Suddenly, every team member could see exactly what needed to happen, when, and how. It set a new standard on clarity and communication for the most complex build on Earth.
4. Origin Story: Cesium’s Open Bet That Paid Off
 3D rendering of Paris looking down the Seine River during the 2024 Olympics.
3D rendering of Paris looking down the Seine River during the 2024 Olympics.What changed? How developers, governments, and tech giants visualize the world.
The moment: Patrick Cozzi built Cesium on a bold idea – that open formats and tools could power a new era of 3D geospatial visualization. His bet paid off. Cesium’s precision streaming technology is now used to visualize everything from global infrastructure to disaster zones, enabling developers, planners, and engineers to interact with complex data in real time. The open approach fostered a massive community (see our story about the first Cesium Developer Conference) and helped turn 3D Tiles – Cesium’s own format – into an industry standard. With its 2024 acquisition by Bentley, Cesium’s technology is bringing infrastructure digital twins to life at an unprecedented scale.
Full story: Leveling Up: How Patrick Cozzi’s Love for Graphics Led to Cesium’s Game-Changing Visualization Tech
5. When Bentley met Cesium: The Inflection Point
What changed? The scale at which infrastructure can be understood.
The moment: After years of close collaboration, Bentley’s 2024 acquisition of Cesium signaled a shared commitment to an open, interoperable future. Together, the companies are enabling digital twins that span everything from buried pipelines to lunar habitats – seamlessly aligning geospatial and engineering data with millimeter precision.
Full story: Cesium Joins Bentley Systems
6. Dublin Fire Brigade Prepares to Ditch Paper
 Digital Twin for Emergency Response, also known as DTER, aims to reduce pre-incident planning time for firefighting.
Digital Twin for Emergency Response, also known as DTER, aims to reduce pre-incident planning time for firefighting.What changed? Emergency response moving from paper trails to real-time digital insight
The moment: At a high-risk industrial site, Dublin Fire Brigade tested a digital twin built with Bentley’s iTwin platform. Instead of sifting through paper binders full of potentially outdated site information, firefighters could instantly access building layouts, sensor data, and hazard information – all in one place. Chief Dennis Keeley and his team are pioneering a smarter, faster approach to emergency response that could set the template for cities around the world. In May, the fire brigade participated in Bentley’s first Urban Tech Challenge in Dublin. The team took the digital twin to the next level and won! Next stop: Bentley’s Year in Infrastructure and going Digital Awards in Amsterdam in October.
Full story: Dublin Fire Brigade Blazes a Trail for Digital Twins in Emergency Response
7. Old Gold Mines Regain Their Shine
 The shift toward smarter, more sustainable mining is accelerating with the help of digital tools and AI.
The shift toward smarter, more sustainable mining is accelerating with the help of digital tools and AI.What changed? Mining’s relationship to its own past.
The moment: As gold prices soar, mining companies are reevaluating old sites once deemed uneconomical. But this means grappling with decades-old data that is often paper-based: core logs, assays, and field notes scattered across siloed archives. With Seequent’s digital tools, companies are digitizing and re-analyzing this legacy information, unlocking insights that had long gone untapped. Suddenly, old mines have new potential. What changed wasn’t the data, but what could be done with it.
Full story: The New Gold Rush: How Digital Tools and AI are Reviving Abandoned Mines
8. Seeing the Good for the Trees
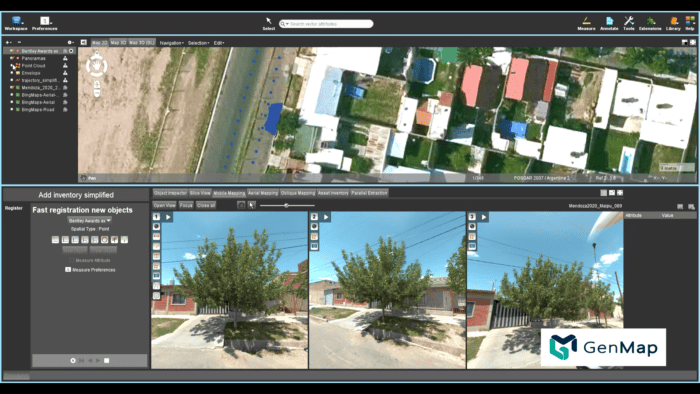 Creating a digital twin of Mendoza’s green infrastructure enabled GenMap to study, classify and analyze more than 600,000 trees. Courtesy of GenMap
Creating a digital twin of Mendoza’s green infrastructure enabled GenMap to study, classify and analyze more than 600,000 trees. Courtesy of GenMapWhat changed? The perception of what counts as critical infrastructure.
The moment: During the COVID-19 pandemic, with lockdowns limiting the workforce available for on-the-ground inspections, a team in Mendoza, Argentina, used Bentley-powered digital twins to map and analyze every tree in its shade-providing urban canopy – over 600,000 in total. With photos captured street by street, planners could remotely assess tree health, model cooling benefits, and guide maintenance priorities. A literal case of data growing on trees, the project redefined what counts as critical infrastructure in a warming world.
9. Iryna Osadcha’s leap of faith
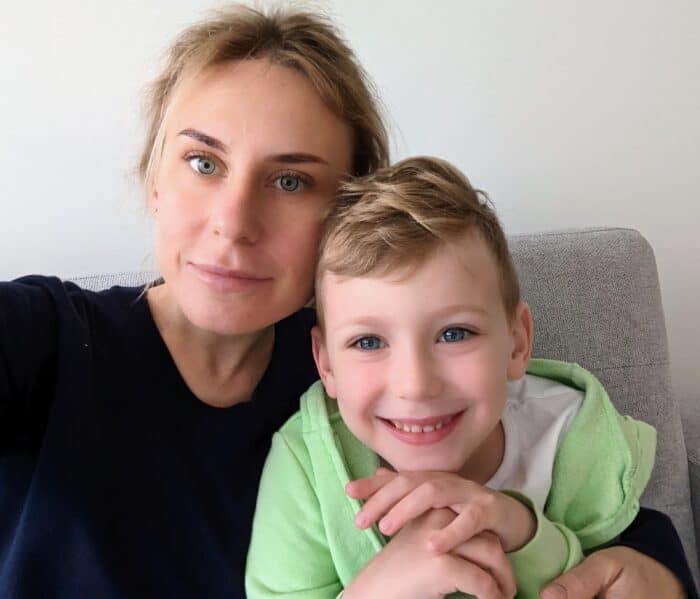 “We were shocked and lost,” said Osadcha, who escaped with her son, Yakiv, to Kaunas, Lithuania. “It wasn’t clear what was going to happen, but I knew we had to move fast.”
“We were shocked and lost,” said Osadcha, who escaped with her son, Yakiv, to Kaunas, Lithuania. “It wasn’t clear what was going to happen, but I knew we had to move fast.”What changed? Turning wartime displacement into urban resilience.
The moment: Fleeing Ukraine with her young son after Russian forces invaded, civil engineer Iryna Osadcha found refuge at Kaunas University of Technology in Lithuania. There, she reshaped her research around digital twins for post-disaster recovery. She now works to keep these virtual models accurate in fast-changing environments – from war zones to disaster-struck cities – so engineers can assess damage, plan interventions, and rebuild more efficiently. For Osadcha, the work is deeply personal.
Sean O’Neill is a seasoned editor, journalist, and science communicator. He spent 14 years at New Scientist and served as the magazine’s People Editor. Sean has written for Google DeepMind, served as communications lead at the Cambridge Centre for AI in Medicine at the University of Cambridge, and worked as a Science Writer for The Alan Turing Institute in London. You can also find his byline on AI stories and profiles on the Bentley blog.